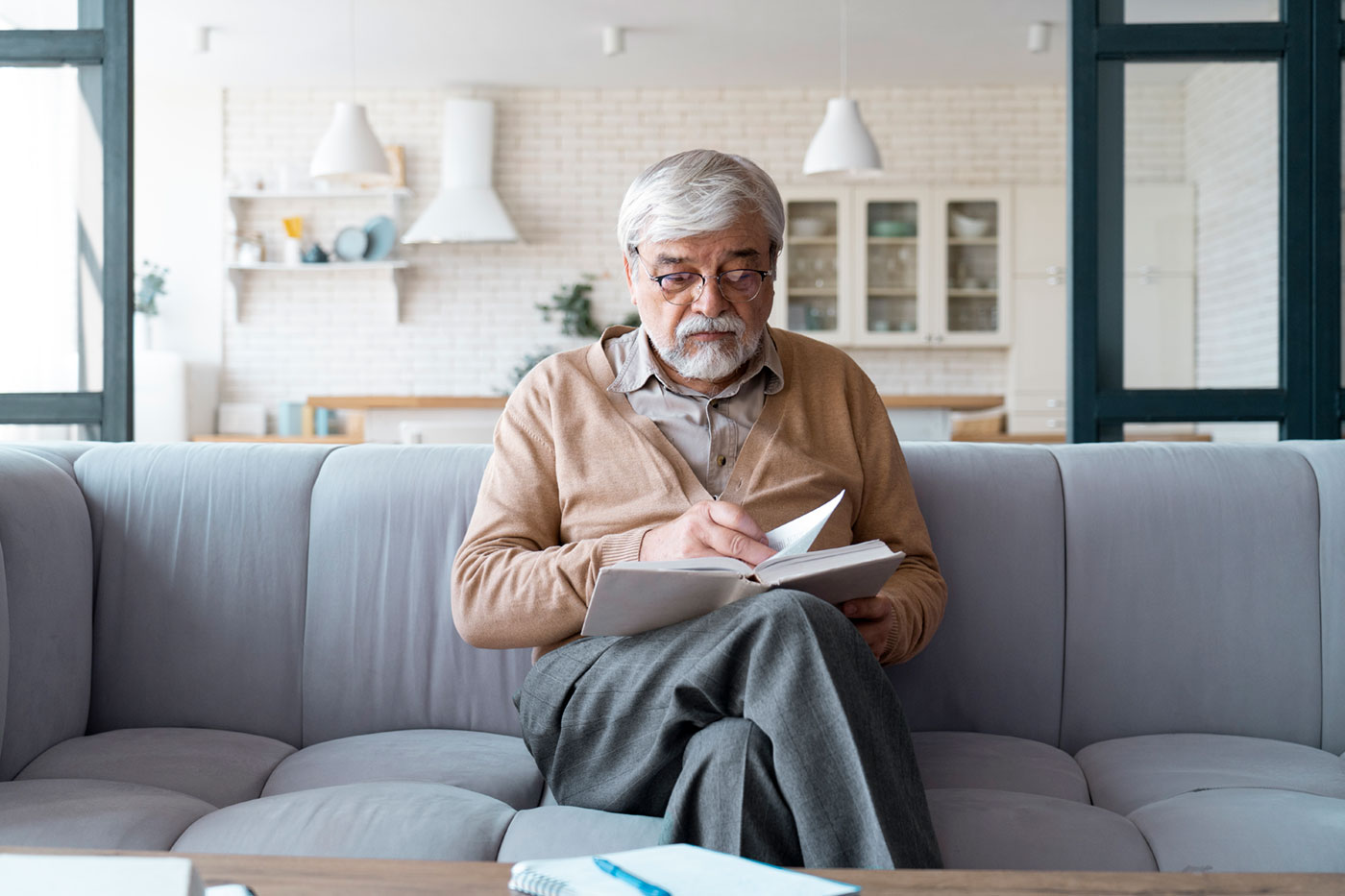
Understanding Dementia (Mate Wareware) in Aotearoa

Dementia, known in te reo Māori as mate wareware
is a broad term that describes a range of symptoms affecting memory, thinking, behavior, and the ability to carry out daily activities. It’s not a single disease but rather a syndrome caused by various underlying conditions, with Alzheimer’s disease being the most common.
*In Aotearoa New Zealand, almost 70,000 Kiwis are currently living with dementia mate wareware, and this number is projected to increase to 170,000 by 2050. Alarmingly, four out of five New Zealanders either know or have known someone affected by the condition.
Key Characteristics of Dementia (Mate Wareware)
People with dementia mate wareware may experience:
- Memory Loss – Difficulty recalling recent events, names, or faces, which typically worsens over time.
- Cognitive Impairments – Struggles with problem-solving, planning, and understanding abstract concepts.
- Communication Problems – Trouble finding the right words, following conversations, or understanding language.
- Behavioural and Emotional Changes – Mood swings, apathy, depression, and irritability are common.
- Impact on Daily Life – Tasks like managing finances, cooking, and navigating familiar places become increasingly challenging.
The Growing Impact of Dementia (Mate Wareware) in New Zealand
Dementia mate wareware disproportionately affects more women than men, with women being around 30% more likely to develop the condition. The economic burden is significant, with the total cost to Aotearoa New Zealand currently estimated at $2.5 billion, projected to reach $5.9 billion by 2050. Residential care accounts for nearly half of this cost, with government spending approximately $1.21 billion annually on care services. Additionally, care partners—often family members—provide over one million hours of unpaid care every week, highlighting the immense social and emotional toll of the condition.
Common Types of Dementia (Mate Wareware)
There are several types of dementia mate wareware, each with distinct characteristics:
- Alzheimer’s Disease – The most prevalent type, marked by the buildup of plaques and tangles in the brain.
- Vascular Dementia – Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often following strokes or small blockages.
- Lewy Body Dementia – Characterized by abnormal protein deposits in the brain, leading to hallucinations and movement difficulties.
- Frontotemporal Dementia – Affects personality, behavior, and language skills, typically occurring between ages 45–65.
- Mixed Dementia – A combination of two or more types, such as Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia.
Notably, dementia mate wareware is increasing at a *faster rate among Māori, Pacific peoples, and Asian populations compared to European New Zealanders, underscoring the need for culturally responsive support and healthcare services.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of dementia mate wareware, including:
- Age – The risk increases significantly after age 65.
- Genetics – A family history of dementia may raise the likelihood of developing it.
- Lifestyle Choices – Poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking can increase the risk.
- Health Conditions – Conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol are linked to a greater risk of vascular dementia.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing dementia mate wareware involves a combination of:
- Cognitive tests and medical history reviews
- Brain imaging, such as MRI or CT scans
- Blood tests to rule out other possible conditions
While there is no cure for most types of dementia, management strategies can help slow progression and improve quality of life, including:
- Medications – Cholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., Donepezil) or Memantine can aid cognitive function.
- Lifestyle Changes – Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and mental stimulation may help slow progression.
- Support Services – Caregivers, support groups, and organisations such as Alzheimer’s New Zealand provide vital resources and assistance.
Living with Dementia (Mate Wareware)
Early diagnosis allows for better planning and treatment, enhancing quality of life for those affected. The support of family, caregivers, and community organisations is essential in helping individuals with dementia mate wareware maintain their independence and well-being.
With the increasing prevalence of dementia mate wareware, it is crucial to foster awareness, provide adequate support, and ensure that healthcare systems are equipped to meet the growing demands of this condition in Aotearoa New Zealand.
*Facts sourced from https://alzheimers.org.nz/explore/facts-and-figures/
image sourced from https://chouneurosurgery.com/condition/dementia/











